前言
本篇文章继续跟着李伟老师学习webgl,主要内容是回顾顶点索引并拓展和学习多着色器使用。
顶点索引
在之前的文章中,我们就提到过这个概念
JS绘制立方体布点
1 | const verticeLib = [ |
至于为什么这么布置点位,大家可以这么理解一下
1 | // v6----- v5 |
我们以立方体的中心点作为原点,那么v0-v7可以依次用上面的点位表示,比如v0的x方向(右边为正)就是1,y方向(上面为正)也是1,z方向(指向我们的方向为正)也是1。剩下的点也都是这样得到位置的。
- 首先看前四组索引:
0, 1:表示连接verticeLib数组中的第 0 个顶点和第 1 个顶点,构成一条边。
1, 2:连接第 1 个顶点和第 2 个顶点,继续构成边。
2, 3:连接第 2 个顶点和第 3 个顶点。
3, 0:连接第 3 个顶点和第 0 个顶点。这四组索引共同构成了立方体的一个面(通常可以认为是顶面或底面)。 - 接着看中间四组索引:
0, 5:连接第 0 个顶点和第 5 个顶点,构成另一条边。
1, 6:连接第 1 个顶点和第 6 个顶点。
2, 7:连接第 2 个顶点和第 7 个顶点。
3, 4:连接第 3 个顶点和第 4 个顶点。这四组索引构成了立方体四个侧面中的其中四个边。 - 最后四组索引:
4, 5:连接第 4 个顶点和第 5 个顶点。
5, 6:连接第 5 个顶点和第 6 个顶点。
6, 7:连接第 6 个顶点和第 7 个顶点。
7, 4:连接第 7 个顶点和第 4 个顶点。这四组索引构成了立方体另一个面(与前面构成的面相对)以及四个侧面中的另外四个边。
通过这样的索引组合,就可以明确地指定哪些顶点连接在一起,从而构建出一个完整的立方体形状。每个索引对应verticeLib数组中的特定位置,通过这些索引可以准确地提取出需要的顶点坐标,进而绘制出立方体的各个面和边。
WEBGL绘制立方体
上面是我们用JS进行绘制的立方体,其实我们可以直接用WEBGL来进行绘制,省去了我们自己使用arr来计算顶点的过程。
顶点数据verticeLib 和顶点索引数据indices 和之前一样
1 | const verticeLib = new Float32Array([ |
顶点数据在webgl缓冲区写入和之前都是一样的
1 | const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); |
视图矩阵和模型矩阵和设置和之前也是一样的
1 | const u_ViewMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_ViewMatrix') |
把顶点索引写入webgl缓冲区
1 | //建立缓冲对象 |
接下来咱们说不一样的地方。
绘图
1 | gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); |
drawElements(mode, count, type, offset) 是使用顶点索引绘图的方法。
- mode 绘图方式
- count 元素数量
- type 缓冲区数据的类型
- offset 当前系列的字节索引位
我们上面用顶点索引画了一个线框
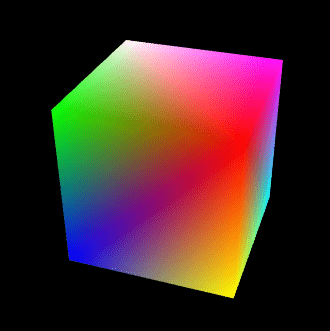
绘制彩色立方体
着色器
1 | <script id="vertexShader" type="x-shader/x-vertex"> |
上面的a_Color 是和a_Position 一一对应的,一个顶点,一个颜色,用attribute 声明的a_Color。
如果整个立方体都是一个颜色,直接在片元着色器里用uniform 声明就好了。
初始化着色器,打开深度测试
1 | import { initShaders } from '../jsm/Utils.js'; |
深度测试可以解决物体的遮挡问题,不然后面的物体可能挡住前面的物体。
建立透视相机和轨道控制器
1 | /* 透视相机 */ |
声明顶点数据vertices 和顶点索引indexes
1 | // v6----- v5 |
vertices中每一行有俩个参数,前面三个是顶点索引,后面三个是颜色,代表了rgb。
将顶点数据写入缓冲区,并将其中的点位和颜色数据分别分配给a_Position 和a_Color
1 | //元素字节数 |
将顶点索引写入缓冲区
1 | // 建立缓冲区对象 |
建立模型矩阵,并传递给片元着色器
1 | const u_ModelMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_ModelMatrix') |
建立投影视图矩阵,并传递给片元着色器
1 | const u_PvMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_PvMatrix') |
用连续渲染的方法绘图
1 | !(function ani() { |
多着色器
到目前为止,我们都是用了一套着色器做的例子,这一套着色器包含了顶点着色器和片元着色器。
在实际开发中,我们是不可能只用一套着色器做项目的,就比如场景里有两个三角形,一个三角形需要着纯色,一个三角形需要着纹理。

接下来我们就拿两个三角形来说一下多着色器的实现方法。
多着色器绘图
准备两套着色器
两套着色器,一套着纯色,一套着纹理。
1 | <!-- 着纯色 --> |
绘制纯色三角形
- 建立程序对象,并应用
1
2
3
4const solidVsSource = document.getElementById('solidVertexShader').innerText
const solidFsSource = document.getElementById('solidFragmentShader').innerText
const solidProgram = createProgram(gl, solidVsSource, solidFsSource)
gl.useProgram(solidProgram)
上面的createProgram() 方法是基于一套着色器建立程序对象的方法:
1 | function createProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource) { |
关于程序对象的概念咱们之前在前面的文章里已经说过。
之前我们的初始化着色器方法initShaders() 只是比上面的方法多了一个应用程序对象的步骤:
1 | gl.useProgram(program); |
我们这里之所以把启用程序的步骤提取出来,是因为一套着色器对应着一个程序对象。
而一个webgl 上下文对象,是可以依次应用多个程序对象的。
通过不同程序对象,可以绘制不同材质的图形。
- 用当前的程序对象绘制图形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14const solidVertices = new Float32Array([
-0.5, 0.5,
-0.5, -0.5,
0.5, -0.5,
])
const solidVertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer()
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, solidVertexBuffer)
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, solidVertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW)
const solidPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(solidProgram, 'a_Position')
gl.vertexAttribPointer(solidPosition, 2, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0)
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(solidPosition)
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3)
因为我们后面还需要绘制一个纹理图形,纹理图形是需要等纹理加载成功才能绘制的。
这会造成两个三角形的异步绘制,这并不是我们想要的,因为一异步,就会把之前三角形的缓冲数据给清理掉,这个原理,我们之前说过。
因此,我需要同步绘制两个三角形。
我先把上面的绘图方法封装到一个函数里,等纹理三角形的图片加载成功了,再执行。
1 | function drawSolid() { |
绘制纹理三角形
纹理三角形的绘制原理和纯色三角形一样,要用一套新的着色器建立一个新的程序对象,然后用这个新的程序对象进行绘图。
1 | function drawTexture(image) { |
同步绘图
当纹理图形加载成功后,进行同步绘图。
1 | const image = new Image() |
多着色器动画
我想给场景中的图形添加一个动画,比如我想让纯色三角形不断的变换颜色。在上面的绘图方法中,很多操作都是不需要重复执行的,比如程序对象在建立之后,就不需要再建立了,后面在绘图的时候再接着用。
给纯色三角形添加一个代表时间的uniform变量
1 | <script id="solidFragmentShader" type="x-shader/x-fragment"> |
程序对象、缓冲对象、从着色器中获取的attribute变量和uniform变量都是不需要重复获取的。
初始化方法
1.把绘制纯色三角形的方法变成初始化方法
1 | function initSolid() { |
2.把绘制纹理三角形的方法变成初始化方法
1 | function initTexture(image) { |
上面已经注释掉的是需要在绘图时重复执行的。
3.把需要重复执行的方法收集一下,用于连续渲染
1 | function render(time = 0) { |
由上可知,在连续渲染时,必须要有的操作:
- clear() 清理画布
- useProgram() 应用程序对象
- bindBuffer() 绑定缓冲区对象
- vertexAttribPointer() 告诉显卡从当前绑定的缓冲区(bindBuffer()指定的缓冲区)中读取顶点数据
- drawArrays() 绘图方法
若attribute变量、uniform变量或者图片发生了变化,那就需要对其进行更新。
4.当纹理图像加载成功后,初始化绘图方法,连续绘图
1 | const image = new Image() |
结语
本篇文章就到这里了,更多内容敬请期待,债见~

.gif)

